- Different Types Of Expansion Slots
- Different Types Of Expansion Slots
- Different Types Of Expansion Slots In A Pc
- List Three Different Types Of Expansion Slots
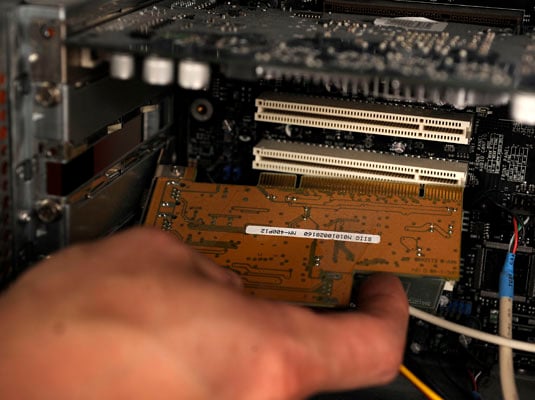
Most modern ATX Motherboards have a maximum of seven PCI or PCI-Express expansion slots, while microATX boards only have a maximum of four. Micro-ATX Motherboard has many advantages over ATX Motherboard, and they are given below. It is compact and smaller than ATX Motherboard, which sports more ports and slots than ATX. That means that—potentially—any storage or disk drive, GPU or port expansion, or low-power gadget that uses a USB connection, could all be mounted on a card plugged into the M.2 slot at the same time. The reality is a little more complicated—for example, a single M.2 slot only has four PCI Express lanes, a quarter of the total generally. There are several types of expansion slots, including AGP, PCIe (also known as PCI express), PCI, and ISA. The smaller card simply needs an empty spot in the case to be mounted to. It does not need to be placed into an expansion slot on the motherboard. Types of Expansion Slots. If you win, Expansion Slots Types then you head to the slots and bet pretty decent stakes in order to get a big win so that you can clear the wagering requirements. The downside to this tactic is that you could lose the first Expansion Slots Types spin and then you don't get to enjoy any playing time at all. PCI-X is a computer bus and expansion card standard that enhances the 32-bit PCI Local Bus for higher bandwidth demanded by servers. It is a double-wide version of PCI, running at up to four times the clock speed, but is otherwise similar in electrical implementation and uses the same protocol.1.
An expansion slot is a laser-cut slot on the blade plate designed to disperse heat and prevent blade deformation caused by overheating. The process of cutting, even under ideal circumstances, involves a lot of friction. While the teeth of the blade are removing material, they are also rubbing against the sides of the kerf and the tip of the tooth rubs against the material in the path of the cut. This friction can generate an amazing amount of heat, enough to singe the wood and even warp the saw blade. The saw blade is quite hot even after cutting; you can easily get burned if you just tap it with your hand for a second when trying to unmount it off the circular saw. The best way to avoid burns is to leave blade running for a minute or two after cutting. However, this does not solve the problem with overheating.
High Temperature and Warping
Different Types Of Expansion Slots
As the temperature of metal increases, it tends to expand, obeying the laws of thermodynamics. However, the temperature of the blade will normally not be consistent across the whole area of the plate, forcing it to expand unevenly. Generally speaking, the plate of the blade gets hotter than the teeth, although the teeth are experiencing the majority of the friction. Even though the teeth have the most friction, they are also are cooled the most by air movement. So, as the plate expands, it needs somewhere to go. Since the outer edge of the plate, where the teeth are attached is not as hot, it isn't expanding as much. Most saw blades have coated teeth, meaning the outer edge is even more solid. That leaves only one direction for the plate to expand, deforming towards the side. This is what causes warping.
Laser-cut Slots
Different Types Of Expansion Slots
Warped saw blades become garbage, so it is helpful to be able to prevent them from expanding unevenly, to avoid the risk of warping. One way in which this is done is to use denser alloys in the blade plate. Another is by laser cut slots periodically through the blade plate. Engineers thought of this idea to allow the expansion of the saw blade 'inside' itself. Although these slots look like they are done for artistic purposes, they aren't; they are there so that they can absorb the expansion of the metal, preventing blade warping.
Different Types Of Expansion Slots In A Pc

Against Vibrations
The blade rotation simultaneously means airflow through the laser-cut plate, which cools it rapidly. That's one benefit of laser-cut slots; they serve as the ventilation slots. If the blade is so hot after you finish the job, imagine what happens during the operation, at the moment when blade slices through the lumber or plastics! These expansion slots also play a part in reducing blade vibration. With many blade designs, the ends of the expansion slots are connected to holes in the center of a saw blade, positioned towards the arbor. These rounded holes are there to reduce vibration. At times, anti-vibration holes are filled with a softer metal, such as copper or brass inserts, which also helps to suppress the vibration of the blade by distributing shock over the entire plate. Such copper plugs inserted at the end of an expansion slot also reduce the noise and help to dissipate heat, extending the life of a saw blade. Vibration is a problem in saw blades, because it, along with warping, are what cause the curved cut marks you see in a freshly cut piece of wood. By reducing vibration and the risk of warping, a blade will run truer, with one tooth faithfully following the path created by the other. That ultimately results in a smoother finish, with less visible tool marking (those curved cut marks).

Heat Cautions
List Three Different Types Of Expansion Slots
When handling saw blades, especially immediately after cutting, be extremely careful of heat. It is not uncommon for blades to become hot enough to burn your fingers. However, blades which are left running after the cut cook quickly; acting as their own ventilator. The expansion slots help with this, acting much like small fan blades to force the air to move. An ability to resist shocks, lower cooling time, less noise and power consumption are just some of the advantages.

An expansion slot is a laser-cut slot on the blade plate designed to disperse heat and prevent blade deformation caused by overheating. The process of cutting, even under ideal circumstances, involves a lot of friction. While the teeth of the blade are removing material, they are also rubbing against the sides of the kerf and the tip of the tooth rubs against the material in the path of the cut. This friction can generate an amazing amount of heat, enough to singe the wood and even warp the saw blade. The saw blade is quite hot even after cutting; you can easily get burned if you just tap it with your hand for a second when trying to unmount it off the circular saw. The best way to avoid burns is to leave blade running for a minute or two after cutting. However, this does not solve the problem with overheating.
High Temperature and Warping
As the temperature of metal increases, it tends to expand, obeying the laws of thermodynamics. However, the temperature of the blade will normally not be consistent across the whole area of the plate, forcing it to expand unevenly. Generally speaking, the plate of the blade gets hotter than the teeth, although the teeth are experiencing the majority of the friction. Even though the teeth have the most friction, they are also are cooled the most by air movement. So, as the plate expands, it needs somewhere to go. Since the outer edge of the plate, where the teeth are attached is not as hot, it isn't expanding as much. Most saw blades have coated teeth, meaning the outer edge is even more solid. That leaves only one direction for the plate to expand, deforming towards the side. This is what causes warping.

Against Vibrations
The blade rotation simultaneously means airflow through the laser-cut plate, which cools it rapidly. That's one benefit of laser-cut slots; they serve as the ventilation slots. If the blade is so hot after you finish the job, imagine what happens during the operation, at the moment when blade slices through the lumber or plastics! These expansion slots also play a part in reducing blade vibration. With many blade designs, the ends of the expansion slots are connected to holes in the center of a saw blade, positioned towards the arbor. These rounded holes are there to reduce vibration. At times, anti-vibration holes are filled with a softer metal, such as copper or brass inserts, which also helps to suppress the vibration of the blade by distributing shock over the entire plate. Such copper plugs inserted at the end of an expansion slot also reduce the noise and help to dissipate heat, extending the life of a saw blade. Vibration is a problem in saw blades, because it, along with warping, are what cause the curved cut marks you see in a freshly cut piece of wood. By reducing vibration and the risk of warping, a blade will run truer, with one tooth faithfully following the path created by the other. That ultimately results in a smoother finish, with less visible tool marking (those curved cut marks).
Heat Cautions
List Three Different Types Of Expansion Slots
When handling saw blades, especially immediately after cutting, be extremely careful of heat. It is not uncommon for blades to become hot enough to burn your fingers. However, blades which are left running after the cut cook quickly; acting as their own ventilator. The expansion slots help with this, acting much like small fan blades to force the air to move. An ability to resist shocks, lower cooling time, less noise and power consumption are just some of the advantages.
An expansion slot is a laser-cut slot on the blade plate designed to disperse heat and prevent blade deformation caused by overheating. The process of cutting, even under ideal circumstances, involves a lot of friction. While the teeth of the blade are removing material, they are also rubbing against the sides of the kerf and the tip of the tooth rubs against the material in the path of the cut. This friction can generate an amazing amount of heat, enough to singe the wood and even warp the saw blade. The saw blade is quite hot even after cutting; you can easily get burned if you just tap it with your hand for a second when trying to unmount it off the circular saw. The best way to avoid burns is to leave blade running for a minute or two after cutting. However, this does not solve the problem with overheating.
High Temperature and Warping
As the temperature of metal increases, it tends to expand, obeying the laws of thermodynamics. However, the temperature of the blade will normally not be consistent across the whole area of the plate, forcing it to expand unevenly. Generally speaking, the plate of the blade gets hotter than the teeth, although the teeth are experiencing the majority of the friction. Even though the teeth have the most friction, they are also are cooled the most by air movement. So, as the plate expands, it needs somewhere to go. Since the outer edge of the plate, where the teeth are attached is not as hot, it isn't expanding as much. Most saw blades have coated teeth, meaning the outer edge is even more solid. That leaves only one direction for the plate to expand, deforming towards the side. This is what causes warping.
Laser-cut Slots
Warped saw blades become garbage, so it is helpful to be able to prevent them from expanding unevenly, to avoid the risk of warping. One way in which this is done is to use denser alloys in the blade plate. Another is by laser cut slots periodically through the blade plate. Engineers thought of this idea to allow the expansion of the saw blade 'inside' itself. Although these slots look like they are done for artistic purposes, they aren't; they are there so that they can absorb the expansion of the metal, preventing blade warping.
Against Vibrations
The blade rotation simultaneously means airflow through the laser-cut plate, which cools it rapidly. That's one benefit of laser-cut slots; they serve as the ventilation slots. If the blade is so hot after you finish the job, imagine what happens during the operation, at the moment when blade slices through the lumber or plastics! These expansion slots also play a part in reducing blade vibration. With many blade designs, the ends of the expansion slots are connected to holes in the center of a saw blade, positioned towards the arbor. These rounded holes are there to reduce vibration. At times, anti-vibration holes are filled with a softer metal, such as copper or brass inserts, which also helps to suppress the vibration of the blade by distributing shock over the entire plate. Such copper plugs inserted at the end of an expansion slot also reduce the noise and help to dissipate heat, extending the life of a saw blade. Vibration is a problem in saw blades, because it, along with warping, are what cause the curved cut marks you see in a freshly cut piece of wood. By reducing vibration and the risk of warping, a blade will run truer, with one tooth faithfully following the path created by the other. That ultimately results in a smoother finish, with less visible tool marking (those curved cut marks).
Heat Cautions
When handling saw blades, especially immediately after cutting, be extremely careful of heat. It is not uncommon for blades to become hot enough to burn your fingers. However, blades which are left running after the cut cook quickly; acting as their own ventilator. The expansion slots help with this, acting much like small fan blades to force the air to move. An ability to resist shocks, lower cooling time, less noise and power consumption are just some of the advantages.